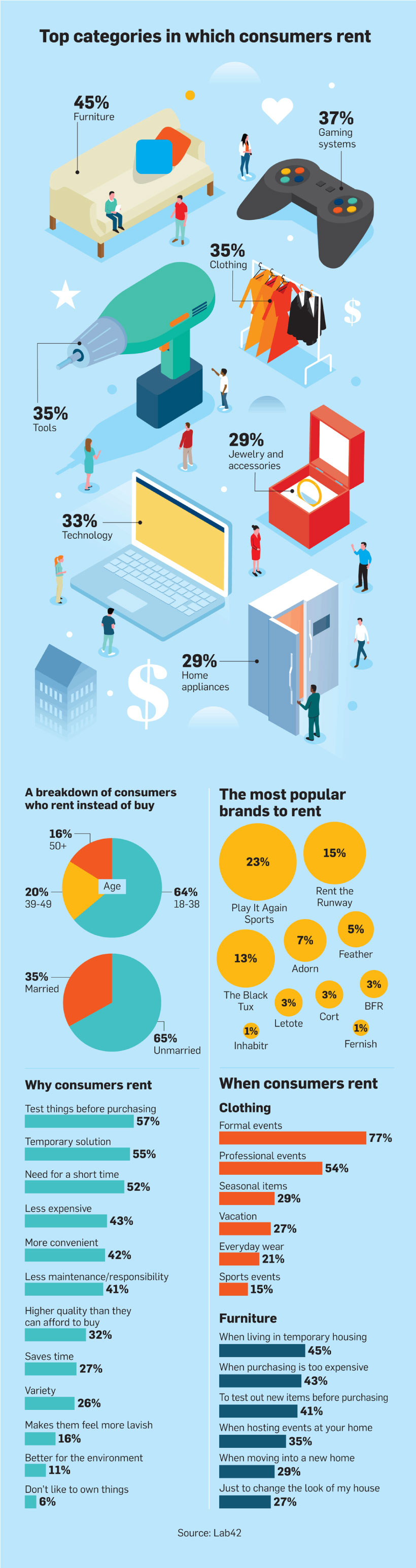
Most recently, this effect has been seen in the retail landscape, where millennial spending habits are setting the tone for the market’s future. Not only does the millennial generation demand the convenience of making instant purchases—but they can now rent almost anything they want, anytime, and anywhere.
Visualizing the Growth of the Rental Economy
Today’s infographic from Adweek takes a deeper look at the consumer goods rental economy, and the potential long-term impact of this shift in buyer behavior. Although the current market for rentals is still in its early stages, the sheer momentum that the industry has gained in the last year is enough to threaten even the largest retailers—forcing them to reconsider their own business models.
The data for the visualization above comes from market research company Lab 42. In a survey of 500 people, they found that 94% of the U.S. population has participated in the sharing economy in one way or another. While the sharing economy spotlight typically shines on global behemoths like Airbnb and Uber, the research used to populate this infographic focuses on renting consumer goods for a short period of time, as a sub-segment of the sharing economy.
The Renting Revolution
Offerings within the rental sector have exploded over the last decade, with furniture being the number one category that consumers rent. According to the infographic, reasons for renting furniture include:
Temporary housing: 45% Expensive upfront costs: 43% Testing products before committing: 41% Hosting events at home: 35% Moving into a new home: 29% Redesigning a house: 27%
Other products that consumers rent include gaming systems, clothes, tools, and technology. Female renters are more likely to rent furniture, clothes, and jewelry, while male renters are more likely to rent tools and gaming systems. Renting goods is predominantly done on an as-needed basis. The Lab 42 report states that for clothing, 77% of respondents indicate that they either rent, or would rent for a formal event.
The End of Ownership?
Despite the common misconception that millennials are driven by emotional needs, the reasons behind why they rent consumer goods are much more pragmatic.
Test things before purchasing: 57% Need a temporary solution: 55% Need an item or a service for a short time-frame : 52% Less expensive than buying: 43% More convenient than buying: 42%
Further, only 6% said that they rent because they do not like owning things. This tells us that the rental economy does not indicate the end of ownership, but rather, provides a strategy for consumers to try before they buy.
Attitudes Towards Sustainability
According to the research, very few millennials choose to rent consumer goods because it is better for the environment. However, Nielsen claim that 73% of millennials are willing to pay more money for sustainable offerings—impacting both retail and rental industries. As evidence of this, Ikea will test a range of subscription-based leasing offers in all 30 of its markets by 2020 in a bid to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and boost its sustainability credentials. If Ikea’s evolving business model is a success, it could open the floodgates for others to follow suit.
A Promising Market
In the clothing rental space, brands like Rent the Runway pave the way, but there has also been an explosion of startups entering the market in the last year. One example is the monthly subscription service Nuuly. The company offers consumers access to over 100 third-party brands and vintage items. Consumers can borrow up to six items a month for $88. Similarly, American Eagle’s Style Drop program rents out the latest collections for a flat monthly fee of $49.95. As more companies incorporate short-term rental services into their offerings, more millennials will shift their behavior from buying to renting—disrupting the traditional retail business model as we know it. With that being said, the impact of millennials having it all, and owning none of it, is yet to be determined. on Media consumption spiked in the early days of the COVID-19 outbreak as Americans actively sought information and entertainment while at home. Whether this changed over the course of 2020 remains unclear, however. To dive deeper into the issue, this infographic explores each generation’s shifts in media consumption habits as the pandemic wore on. Further below, we’ll also examine which media sources Americans deemed to be the most trustworthy, and why consumption habits may have changed for good.
Changes in American Media Consumption, by Generation
The data in this infographic comes from two surveys conducted by Global Web Index (GWI). The first was completed in April 2020 (N=2,337) and asked participants a series of questions regarding media consumption during COVID-19. To see how consumption had changed by the end of the year, the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation commissioned GWI to complete a follow-up survey in December 2020 (N=2,014). The following tables provide a summary of the results.
Gen Z
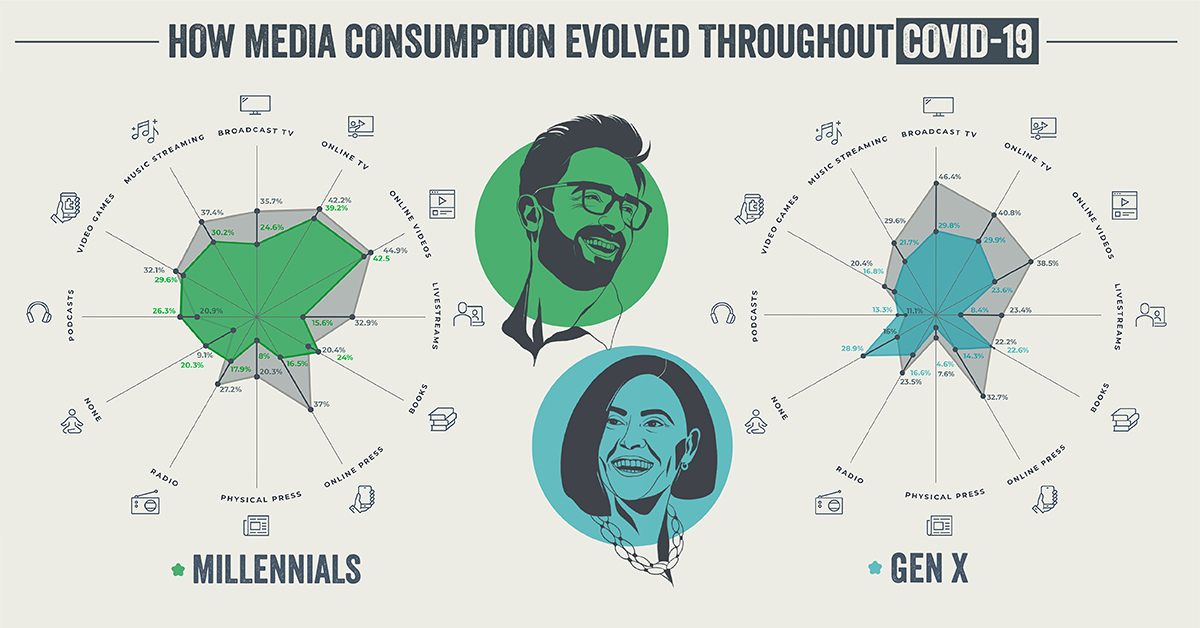
Unsurprisingly, a significant percentage of Gen Z reported an increase in digital media consumption in April 2020 in comparison to pre-pandemic habits. This bump was driven by higher use of online videos, video games, and online TV/streaming films. By December 2020, these media categories became even more popular with this cohort. Most notably, podcasts saw the highest increase, jumping almost 15% by the end of the year. The popularity of traditional outlets like broadcast TV and radio declined from their April 2020 highs, though they are still up relative to pre-pandemic levels for Gen Z survey respondents.
Millennials
Results from the December 2020 survey show that Millennials trimmed their media consumption from earlier in the year. This was most apparent in news outlets (online and physical press), which saw double digit declines in popularity relative to April. Books and podcasts were the only two categories to capture more interest from Millennials over the time period. It’s also worth noting that the percentage of respondents who said “none” for media consumption rose to 20.3%, up significantly from 9.1% in April. Possible factors for the increase in “none” responses include easing government restrictions and a return to more normal work schedules.
Gen X
The media consumption habits of Gen X developed similarly to Millennials over the year. Broadcast TV and online press saw the largest declines over the time period, while once again, podcasts and books were the only two categories to capture more interest relative to April. The percentage of respondents reporting “none” rose to 28.9%—a slightly higher share than that of Millennials.
Boomers
Media consumption trends among Baby Boomers were mixed, with some categories increasing and others decreasing since April. Broadcast TV saw the biggest decline in usage of all media types, but remained the most popular category for this cohort. Boomers also had the largest share of “none” respondents in both studies (23.0% in April and 31.0% in December).
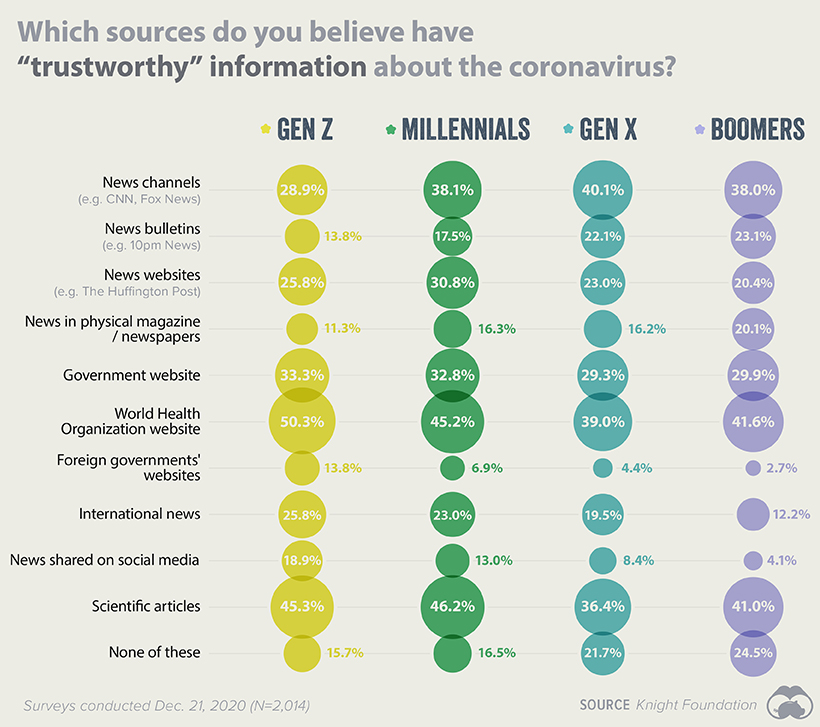
Where do Americans Go For Trustworthy News?
To learn more about American media consumption—particularly when it came to staying updated on the pandemic—survey respondents were asked to confirm which of the following sources they found trustworthy.
The deviations between each generation don’t appear to be too drastic, but there are some key takeaways from this data. For starters, Gen Z appears to be more skeptical of mainstream news channels like CNN, with only 28.9% believing them to be trustworthy. This contrasts the most with Gen X, which saw 40.1% of its respondents give news channels the thumbs up. This story is flipped when we turn to the World Health Organization (WHO). Gen Z demonstrated the highest levels of trust in information published by WHO, at 50.3% of respondents. Only 39.0% of Gen X could say the same. By far the least trustworthy source was foreign governments’ websites. This category had the lowest average approval rating across the four generations, and scored especially poor with Boomers.
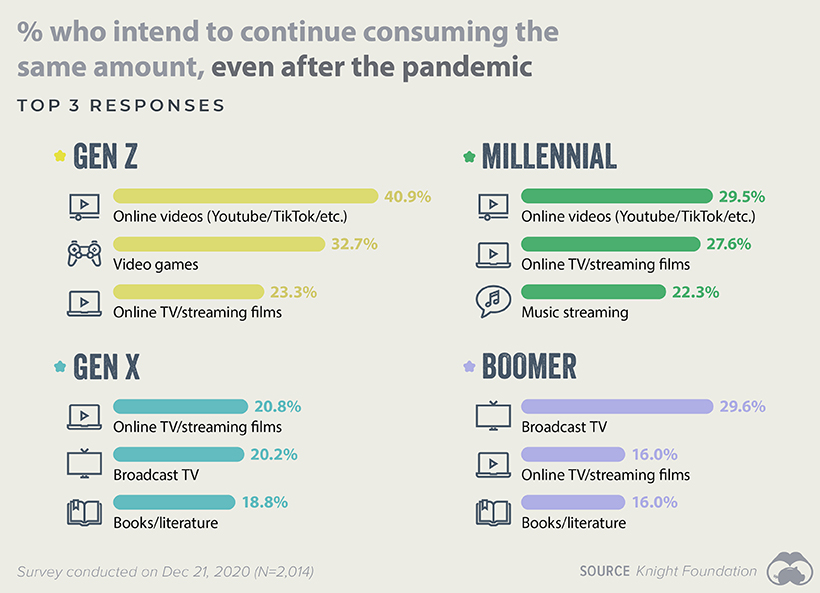
The Lasting Effects of the Pandemic
Habits that were picked up during 2020 are likely to linger, even as life finally returns to normal. To find out what’s changed, respondents were asked which categories of media they expected to continue consuming in elevated amounts. The chart below shows each generation’s top three responses.
Note that the top three for both Gen Z and Millennials are all digital and online categories (video games can be played offline, but the majority of popular titles are online). This contrasts with the preferences of Gen X and Boomers, who appear to be sticking with more traditional outlets in broadcast TV and books. With consumption habits of younger and older Americans moving in opposite directions, advertisers and media companies will likely need a clear understanding of their target audiences in order to be successful.