Today’s chart breaks down the differences in the composition of wealth between middle income, upper income, and ultra wealthy (top 1%) of American households to help us better understand the building blocks that make up net worth. Let’s dive in.
Middle Income: Home is Where the Wealth is
It’s no surprise that the principal residence is the cornerstone of net worth for most Americans in the middle class. For households that fall in this wide range ($0 to $471k of net worth) the combination of housing and pension accounts make up nearly 80% of total wealth on average. Assets like stocks and mutual funds only make up about 4% of wealth in this income bracket, partially mirroring the trend of lower stock market participation in recent years. As we move up the income ladder, however, this situation changes quite a bit.
Upper Income: A Diversified Portfolio
If a household has a net worth that ranges between $471,000 and $10.2 million, it is considered to fall in the upper income band above. This represents the 20% richest households in the U.S., minus the top 1%, which are put in a separate bracket. For this group, the principal residence makes up a smaller slice of the wealth pie. Instead, we see a higher mix of financial assets like stocks and mutual funds, as well as business equity and real estate. Almost half of households in this group own real estate in addition to their principal residence. As households become wealthier, we tend to see a lower share of liquid assets as compared with the other components of net worth.
The Top 1%: The Business Equity Bulge
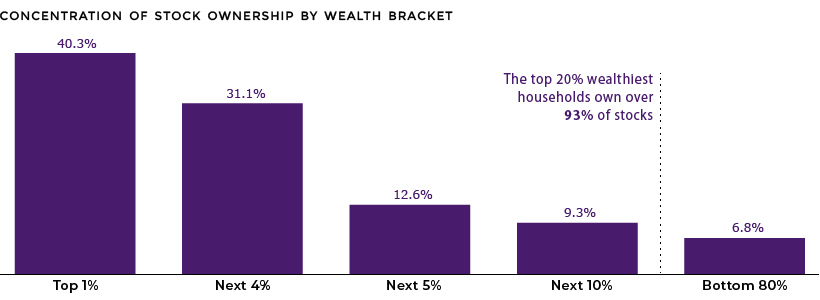
In the richest 1% of households, the principal residence makes up a mere 7.6% of assets. At this stage, almost half of assets fall under the category of business equity and real estate. One of the more prominent features of the ultra rich wealth bracket is a much higher level of financial asset ownership. In fact, the top 1% of households own over 40% of stocks.
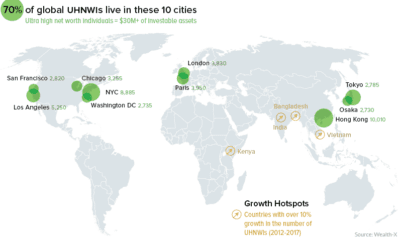
As well, this tiny group of ultra wealthy households earns 22% of total income, up from 8% in the 1970s. on A lagging stock market dented these fortunes against high interest rates, energy shocks, and economic uncertainty. But some of the world’s billionaires have flourished in this environment, posting sky-high revenues in spite of inflationary pressures. With data from Forbes Real-Time Billionaires List, we feature a snapshot of the richest people in the world in 2023.
Luxury Mogul Takes Top Spot
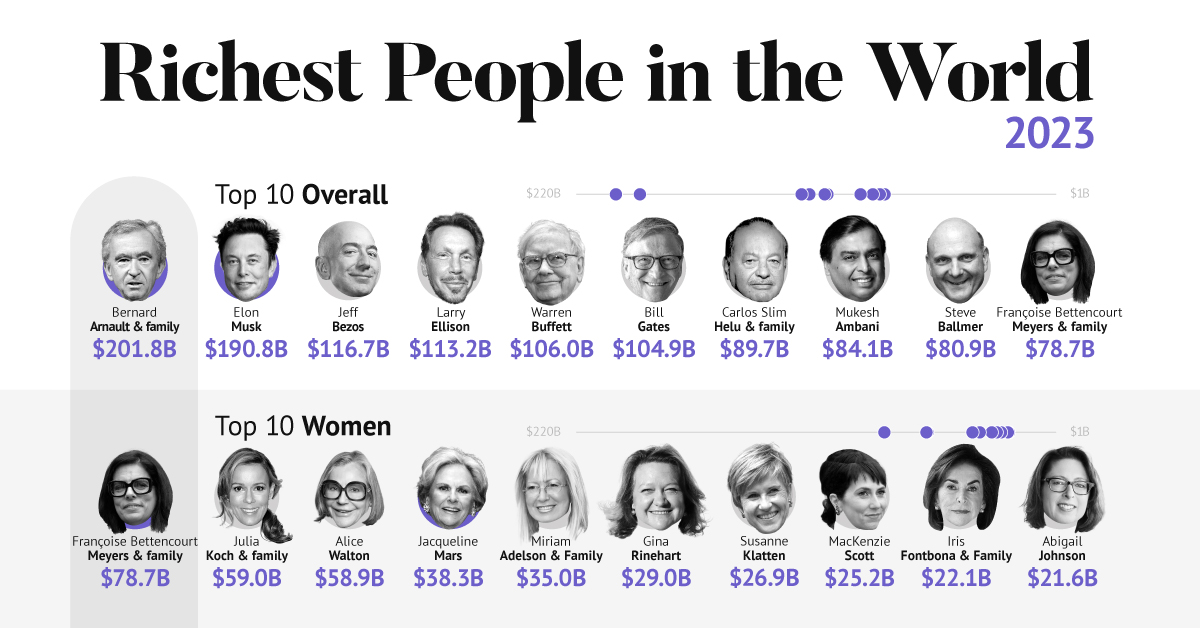
The world’s richest person is France’s Bernard Arnault, the chief executive of LVMH.
With 75 brands, the luxury conglomerate owns Louis Vuitton, Christian Dior, and Tiffany. LVMH traces back to 1985, when Arnault cut his first major deal with the company by acquiring Christian Dior, a firm that was struggling with bankruptcy.
Fast-forward to today, and the company is seeing record profits despite challenging market conditions. Louis Vuitton, for instance, has doubled its sales in four years.
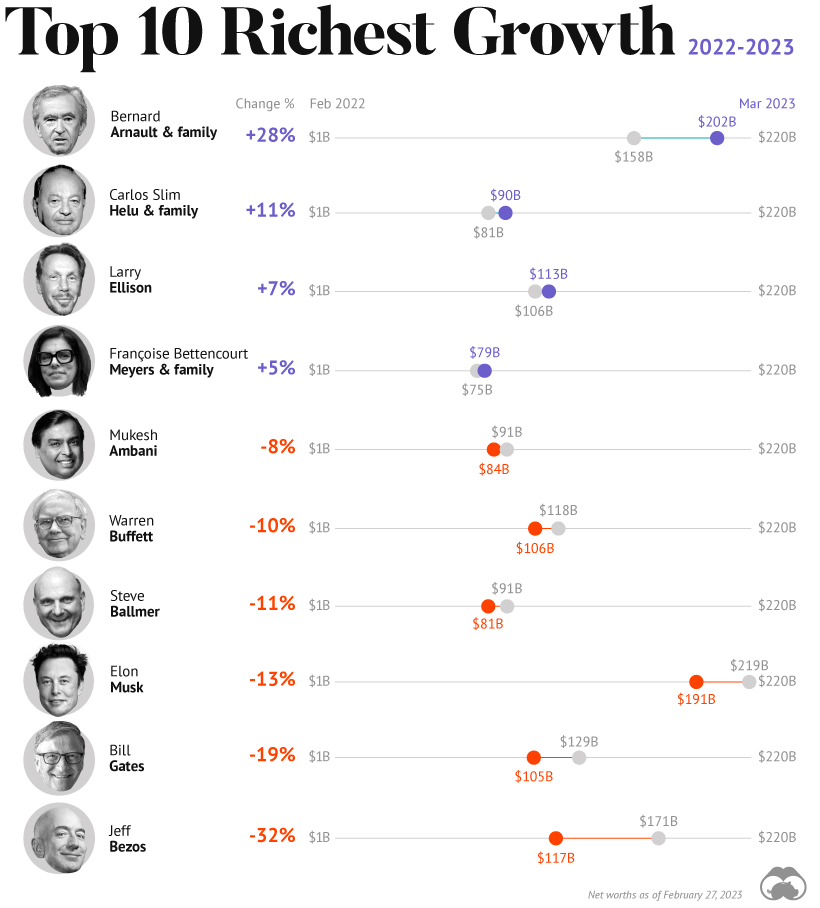
In the table below, we show the world’s 10 richest people with data as of February 27, 2023:
Elon Musk, the second-wealthiest person in the world has a net worth of $191 billion. In October, Musk took over Twitter in a $44 billion dollar deal, which has drawn criticism from investors. Many say it’s a distraction from Musk’s work with Tesla.
While Tesla shares have rebounded—after falling roughly 70% in 2022—Musk’s wealth still sits about 13% lower than in March of last year.
Third on the list is Jeff Bezos, followed by Larry Ellison. The latter of the two, who founded Oracle, owns 98% of the Hawaiian island of Lanai which he bought in 2012 for $300 million.
Fifth on the list is Warren Buffett. In his annual letter to shareholders, he discussed how Berkshire Hathaway reported record operating profits despite economic headwinds. The company outperformed the S&P 500 Index by about 22% in 2022.
How Fortunes Have Changed
Given multiple economic crosscurrents, billionaire wealth has diverged over the last year. Since March 2022, just four of the top 10 richest in the world have seen their wealth increase. Two of these are European magnates, while Carlos Slim Helu runs the largest telecom firm in Latin America. In fact, a decade ago Slim was the richest person on the planet. Overall, as the tech sector saw dismal returns over the year, the top 10 tech billionaires lost almost $500 billion in combined wealth.
Recent Shakeups in Asia
Perhaps the most striking news for the world’s richest centers around Gautam Adani, formerly the richest person in Asia. In January, Hindenburg Research, a short-selling firm, released a report claiming that the Adani Group engaged in stock manipulation and fraud. Specifically, the alleged the firm used offshore accounts to launder money, artificially boost share prices, and hide losses. The Adani Group, which owns India’s largest ports—along with ports in Australia, Sri Lanka, and Israel—lost $100 billion in value in the span of a few weeks. Interestingly, very few Indian mutual funds hold significant shares in Adani Group, signaling a lack of confidence across India’s market, which was also cited in Hindenburg’s report. As a result, Mukesh Ambani has climbed to Asia’s top spot, controlling a $84 billion empire that spans from oil and gas and renewable energy to telecom. His conglomerate, Reliance Industries is the largest company by market cap in India.