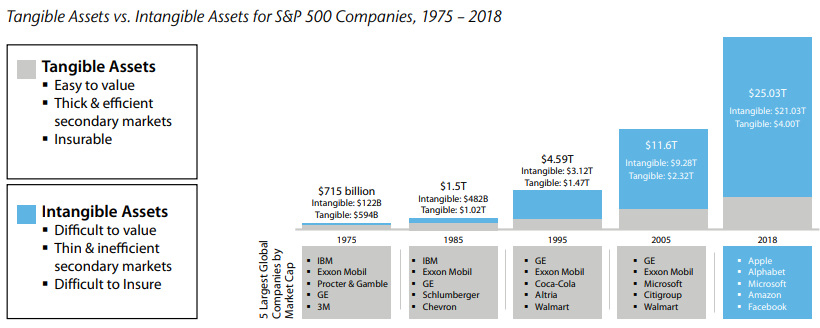
In 2018, intangible assets for S&P 500 companies hit a record value of $21 trillion. These assets, which are not physical in nature and include things like intellectual property, have rapidly risen in importance compared to tangible assets like cash. Today’s infographic from Raconteur highlights the growth of intangible asset valuations, and how senior decision-makers view intangibles when making investment decisions.
Tracking the Growth of Intangibles
Intangibles used to play a much smaller role than they do now, with physical assets comprising the majority of value for most enterprise companies. However, an increasingly competitive and digital economy has placed the focus on things like intellectual property, as companies race to out-innovate one another. To measure this historical shift, Aon and the Ponemon Institute analyzed the value of intangible and tangible assets over nearly four and a half decades on the S&P 500. Here’s how they stack up:
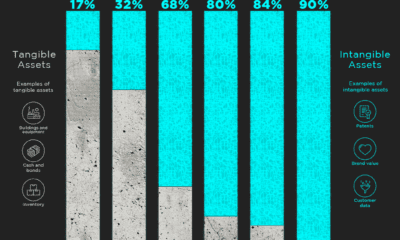
Source: Aon In just 43 years, intangibles have evolved from a supporting asset into a major consideration for investors – today, they make up 84% of all enterprise value on the S&P 500, a massive increase from just 17% in 1975.
The Largest Companies by Intangible Value
Digital-centric sectors, such as internet & software and technology & IT, are heavily reliant on intangible assets. Brand Finance, which produces an annual ranking of companies based on intangible value, has companies in these sectors taking the top five spots on the 2019 edition of their report. Note: Percentages may exceed 100% due to rounding. Pharma and healthcare companies are also prominent on the list, comprising four of the top 20. Their intangible value is largely driven by patents, as well as mergers and acquisitions. Johnson & Johnson, for example, reported $32B in patents and trademarks in their latest annual report.
A Lack of Disclosure
It’s important to note that Brand Finance’s ranking is based on both disclosed intangibles—those that are reported on a company’s balance sheet—and undisclosed intangibles. In the ranking, undisclosed intangibles were calculated as the difference between a company’s market value and book value. The majority of intangibles are not reported on balance sheets because accounting standards do not recognize them until a transaction has occurred to support their value. While many accounting managers see this as a prudent measure to stop unsubstantiated asset values, it means that many highly valuable intangibles never appear in financial reporting. In fact, 34% of the total worth of the world’s publicly traded companies is made up of undisclosed value. —David Haigh, CEO of Brand Finance Brand Finance believes that companies should regularly value each intangible asset, including the key assumptions management made when deriving their value. This information would be extremely useful for managers, investors, and other stakeholders.
A Key Consideration
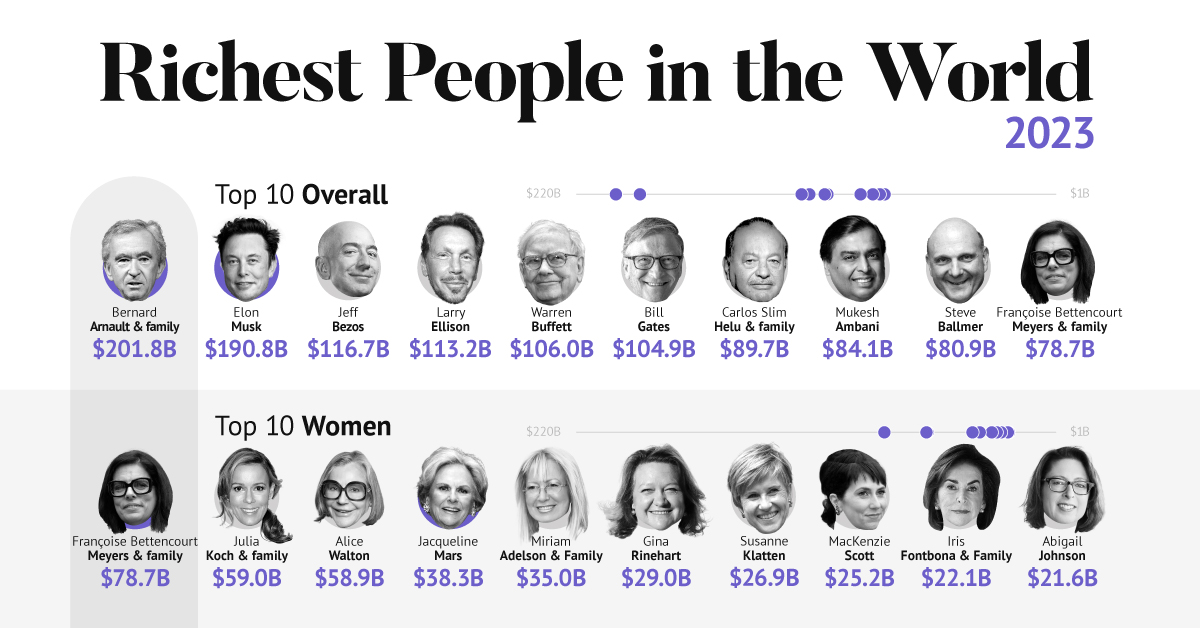
Investment professionals certainly agree on the importance of intangibles. In a survey of institutional investors by Columbia Threadneedle, it was found that 95% agreed that intangible assets contain crucial information about the future strength of a company’s business model. Moreover, 98% agree that more transparency would be beneficial to their assessment of intangible assets. In the absence of robust reporting, Columbia Threadneedle believes active managers are well equipped to understand intangible asset values due to their access to management, relationships with key opinion leaders, and deep industry expertise. By undertaking rigorous analysis, managers may uncover hidden competitive advantages—and generate higher potential returns in the process. on A lagging stock market dented these fortunes against high interest rates, energy shocks, and economic uncertainty. But some of the world’s billionaires have flourished in this environment, posting sky-high revenues in spite of inflationary pressures. With data from Forbes Real-Time Billionaires List, we feature a snapshot of the richest people in the world in 2023.
Luxury Mogul Takes Top Spot
The world’s richest person is France’s Bernard Arnault, the chief executive of LVMH.
With 75 brands, the luxury conglomerate owns Louis Vuitton, Christian Dior, and Tiffany. LVMH traces back to 1985, when Arnault cut his first major deal with the company by acquiring Christian Dior, a firm that was struggling with bankruptcy.
Fast-forward to today, and the company is seeing record profits despite challenging market conditions. Louis Vuitton, for instance, has doubled its sales in four years.
In the table below, we show the world’s 10 richest people with data as of February 27, 2023:
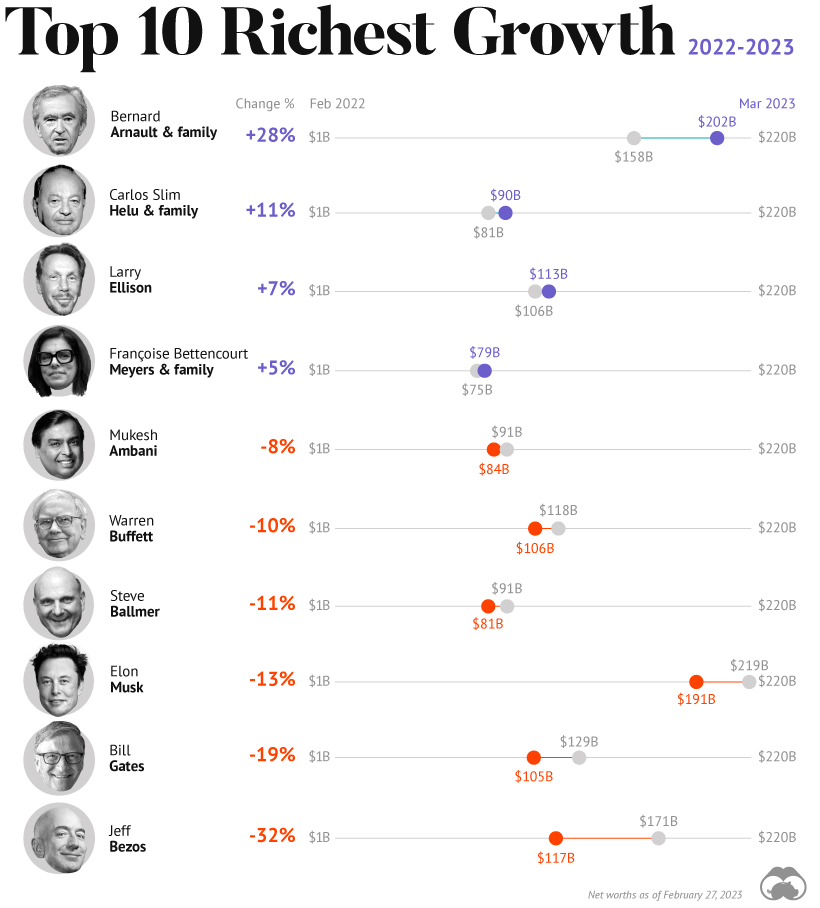
Elon Musk, the second-wealthiest person in the world has a net worth of $191 billion. In October, Musk took over Twitter in a $44 billion dollar deal, which has drawn criticism from investors. Many say it’s a distraction from Musk’s work with Tesla.
While Tesla shares have rebounded—after falling roughly 70% in 2022—Musk’s wealth still sits about 13% lower than in March of last year.
Third on the list is Jeff Bezos, followed by Larry Ellison. The latter of the two, who founded Oracle, owns 98% of the Hawaiian island of Lanai which he bought in 2012 for $300 million.
Fifth on the list is Warren Buffett. In his annual letter to shareholders, he discussed how Berkshire Hathaway reported record operating profits despite economic headwinds. The company outperformed the S&P 500 Index by about 22% in 2022.
How Fortunes Have Changed
Given multiple economic crosscurrents, billionaire wealth has diverged over the last year. Since March 2022, just four of the top 10 richest in the world have seen their wealth increase. Two of these are European magnates, while Carlos Slim Helu runs the largest telecom firm in Latin America. In fact, a decade ago Slim was the richest person on the planet. Overall, as the tech sector saw dismal returns over the year, the top 10 tech billionaires lost almost $500 billion in combined wealth.
Recent Shakeups in Asia
Perhaps the most striking news for the world’s richest centers around Gautam Adani, formerly the richest person in Asia. In January, Hindenburg Research, a short-selling firm, released a report claiming that the Adani Group engaged in stock manipulation and fraud. Specifically, the alleged the firm used offshore accounts to launder money, artificially boost share prices, and hide losses. The Adani Group, which owns India’s largest ports—along with ports in Australia, Sri Lanka, and Israel—lost $100 billion in value in the span of a few weeks. Interestingly, very few Indian mutual funds hold significant shares in Adani Group, signaling a lack of confidence across India’s market, which was also cited in Hindenburg’s report. As a result, Mukesh Ambani has climbed to Asia’s top spot, controlling a $84 billion empire that spans from oil and gas and renewable energy to telecom. His conglomerate, Reliance Industries is the largest company by market cap in India.