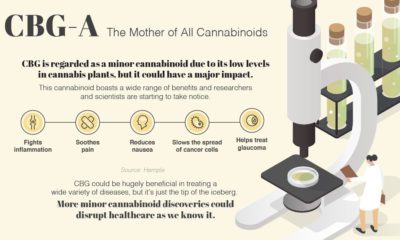
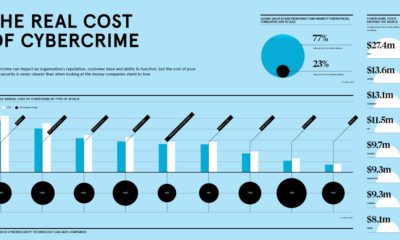
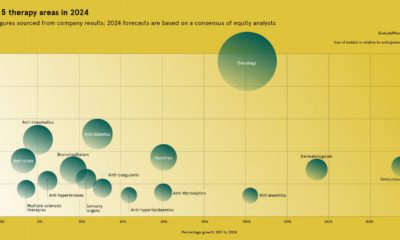
Is there a prospect of stopping – or even slowing – the spread of this debilitating disease?
What You Need to Know About Cancer
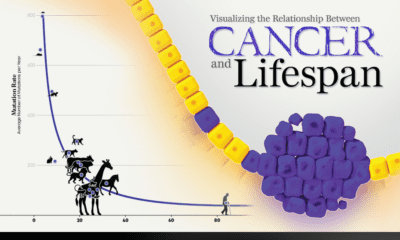
The below infographic from Healthgrad shows that although there have been huge advancements in the understanding of how cancers behave and the development of more effective treatments, there is still no single “cure” for cancer. That said, there are some very promising advances in cancer treatment in progress, and we highlight some thoughts on gaining exposure to these companies later on in the article.
A Global Epidemic
As the infographic points out, we all have cancer cells in our bodies, which our immune systems are responsible for fighting off. Problems arise when these cells are triggered by certain external and internal factors, such as exposure to environmental toxins, viruses, or the natural process of aging. Once these cancer cells are triggered, they begin to multiply rapidly and overwhelm the immune system.
No Single Cure
Cancer is not a single disease, so there can be no single cure. There are actually more than 100 different forms of verified cancerous diseases, however some sources claim this number is much higher. New discoveries about the onset and behavior of cancer are being made all the time, and they are leading to the development of more effective therapies. For example, it was recently discovered that there are multiple subtypes of breast cancer, which may occur at the same time within a patient and have various degrees of responsiveness to different treatments. Findings such as this are driving new forms of more personalized diagnostic and treatment methods, such as vaccines, immunotherapy products, and targeted therapies.
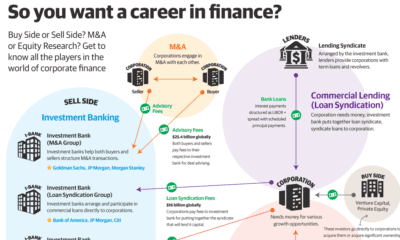
How to Invest in a Cure for Cancer
1.) Prepare to be patient: Currently we are seeing a shift in medical innovation, whereby smaller biotech companies are producing game-changing breakthrough treatments in relatively new fields of oncology such as targeted immunotherapy. Investing in these smaller biotech companies can produce huge returns, but the risk is also high. If a promising biotech startup doesn’t end up getting its product approved by the FDA, the stock price will likely plummet. Another point to keep in mind is that these stocks tend to be quite volatile along the road to marketability. Patience is a virtue when it comes to investing in pharmaceutical companies, and it can take stocks up to five or ten years to reach their full potential. 2.) Diversify among therapies: Today, large pharmaceutical companies are bringing the latest cancer therapy products to market, while smaller biotech companies are working on the next wave of innovative new cancer therapies. A good strategy is to diversify investments by seeking opportunities in both the current and future waves of cancer treatment innovation. Bear in mind that many big pharma companies are actively acquiring smaller biotechs and will continue to do so over the coming years. 3.) Opportunities in acquisitions: In recent years, corporate interest in startups that are developing cancer therapies has been increasing. According to CB Insights, corporate-backed deals in cancer-focused startups increased from around 30 in 2012 to nearly 50 in 2016 (as of October 2016). And it’s not just big pharma that’s taken notice: tech companies such as Google and IBM have entered this space recently, investing millions into startups developing immune-oncology and targeted therapy treatments. Among the most notable deals:
Biopharma company Celgene has been the most active investor in cancer therapy startups, backing 16 companies in the last five years including Cleave Biosciences ($37 million Series B round) and Quanticel Pharmaceuticals ($485 million acquisition) in 2015. Pharma company AbbVie acquired Stemcentrx for $10.2 billion in Q2 2016, one of the largest acquisitions of a VC-backed company in history. Drug development startup Petra Pharma was backed by five of the top corporate investors in a $48 million Series A round, including AbbVie Biotech Ventures, Eli Lilly & Co, Johnson & Johnson Innovation, Pfizer Venture Investments, and WuXi PharmaTech – as well as IBM Watson Group.
Preventive vs. Curative
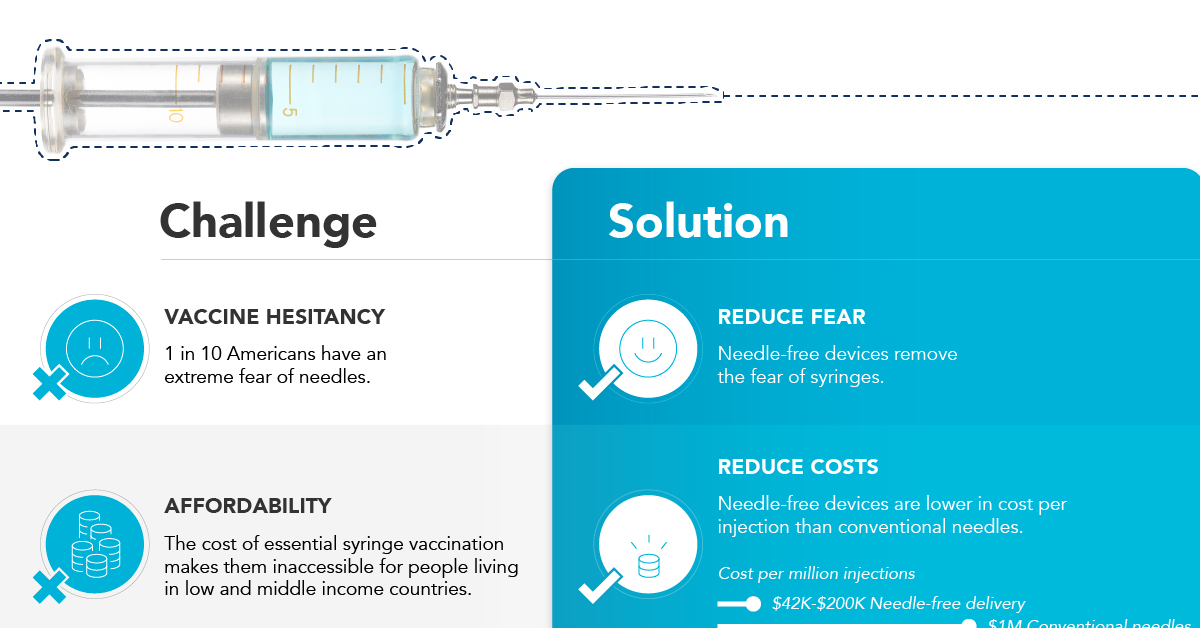
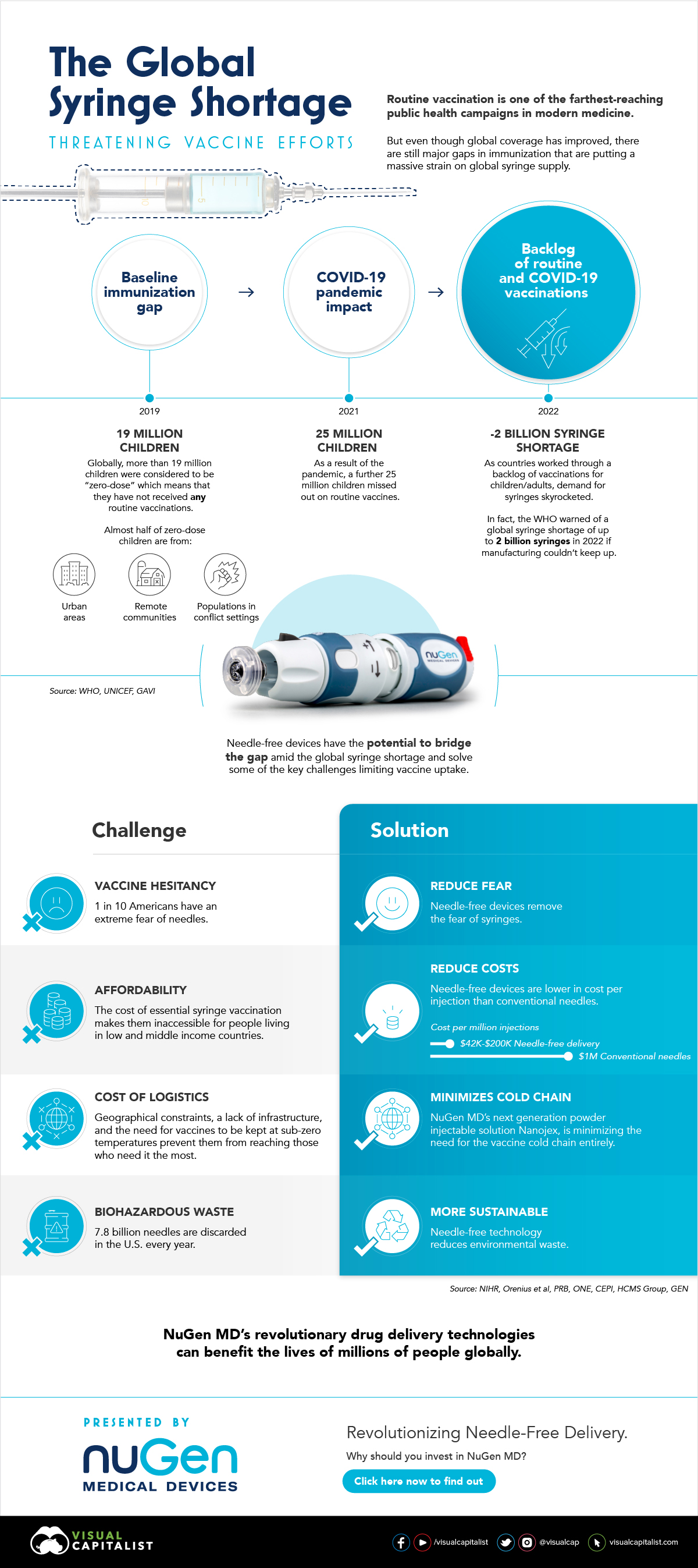
Most cancers, once diagnosed, cost hundreds of thousands of dollars to treat. Many health care professionals in the field of oncology have argued that the way money is currently spent on cancer treatment is not sustainable. Their stance is that more funding should be allocated to preventive rather than curative measures. For example, granting widespread access to vaccinations against certain prevalent cancers – such as for Hepatitis B, the leading cause of liver cancer, and for HPV, the leading cause of cervical cancer – could go a long way to preventing the onset of this devastating disease. on In the above infographic from NuGen Medical Devices, we explore the factors leading to the syringe shortage and take a look at the company’s innovative needle-free solution that could play an important role in closing the immunization gap.
The Immunization Gap
Even before the COVID-19 pandemic, millions of people around the world struggled to get access to routine vaccinations. In fact, as of 2019 more than 19 million children around the world were considered to be “zero-dose” which means that they did not receive any routine vaccinations. Moreover, when the COVID-19 pandemic hit, global immunization dropped even further with 25 million children missing out on routine vaccines in 2021 alone.
Why is Immunization So Important?
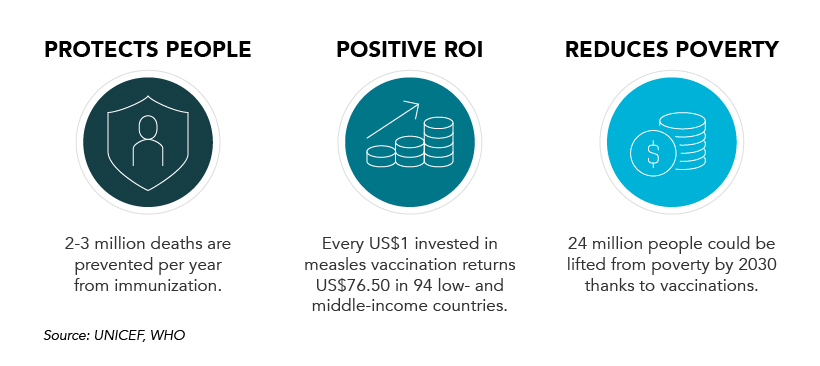
Vaccinations prevent against over 20 life-threatening diseases and save between 2-3 million deaths per year, making them—as the WHO describes—the foundation of healthcare systems and an indisputable human right. As countries work through a backlog of vaccinations to close the immunization gap that has worsened since the pandemic, demand for syringes has significantly increased.
The Result: A Global Syringe Deficit
In 2022, the WHO warned that we could see a shortage of up to 2 billion syringes if manufacturing can’t keep up. This could result in the severe disruption to routine vaccinations and promote unsafe recycling of syringes in order to administer vaccines. But the issue goes far beyond a supply shortage of syringes. COVID-19 has brought conventional syringe vaccines into sharp focus, with many criticizing the challenges associated with them. With conventional needles facing so many challenges, it’s no surprise that investors are taking interest in viable alternatives. What’s more, these alternatives don’t just apply to vaccinations, they can also work for people with diabetes, dentists, and pet care.
Enter Needle-free Devices from NuGen MD
Needle-free devices have the potential to bridge the gap in immunization amid the global syringe shortage, solve some of the key challenges limiting vaccine uptake, and more importantly, benefit the lives of millions of people.
How Do They Work?
NuGen’s needle-free devices use a simple spring-loaded mechanism which uses pressure to release the liquid drug and penetrate the skin. In less than one-tenth of a second, the drug is dispensed more safely and evenly compared to needle syringes. It’s also virtually painless and leaves no mark on the skin.
Interested in investing in NuGen Medical Devices? To learn more about their plans to pioneer the future of needle-free drug delivery, click this link now.