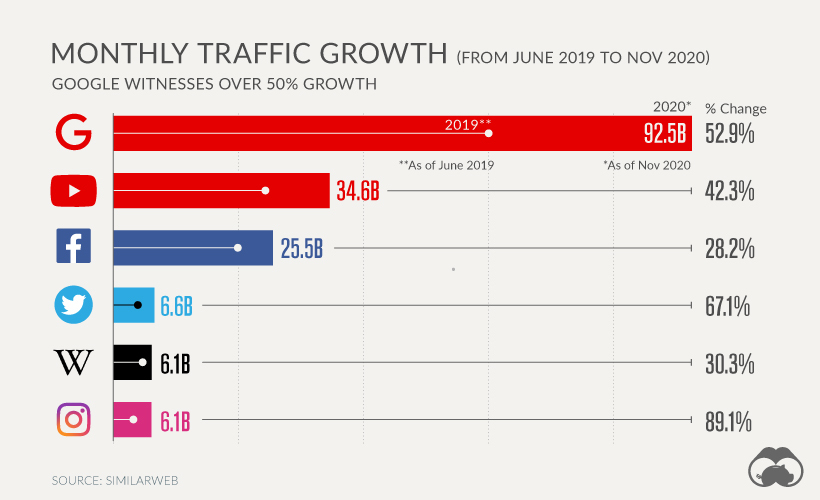
If you spend any time online, it’s likely you’re familiar with some of the world’s most visited websites. On today’s internet, a handful of giants have unmatched dominance. Top Three Websites (Monthly visits):
Google: 92.5 billion YouTube: 34.6 billion Facebook: 25.5 billion
Together, the top three websites rake in 152 billion visits monthly, outpacing the next 47 websites combined. What’s more, as the pandemic transformed everything from the way we work, learn, communicate, and shop—a majority of these activities migrated online. In this new visualization, we look at the most visited websites around the world, drawing data from SimilarWeb (as of November 2020).
The Top Global Websites
Servicing over two trillion search queries annually through its network, Alphabet-owned Google ranks highest with its flagship domain, Google.com. Google derives approximately 80% of its earnings from ad revenues. Coming in second, social networking platform Facebook has a user base of 2.7 billion. On average, users spend 34 minutes on the site daily, while 36% of users say it’s also where they get their news—higher than any other social network. As the leading search engine in China, Baidu (#7) received 5.6 billion visitors in November. Baidu is also branching out its business— venturing into electric vehicles (EVs) in a partnership with China-based automaker Geely. As video conferencing vaulted in demand during the pandemic, Zoom (#15), launched into the most visited websites with 2.7 billion visitors monthly. Similarly, TikTok (#43) became a freshly minted addition.
The Most Visited Websites, By Country of Origin
With 27 sites on the list, the U.S. remains a dominant player. While its reach is highly concentrated on a global level, just a handful of companies own a majority of these sites. See the static version of each regional graphic here. China holds five top websites: Baidu (#7), QQ (#34), Bilibili (#42), TikTok (#43), and AliExpress (#47). The Tencent-owned QQ.com, ranks as the top news site in China, with over 981 million monthly visits. Like WeChat, QQ also provides a popular messaging platform. Just four of the most visited websites globally are based in both Russia and Japan, while the rest of the world account for 10 top sites altogether.
Reaching New Heights
While global internet patterns are clearly dominated by a few titans, what can we make of their recent traffic growth? Between June 2019 and November 2020, Google’s monthly visitors increased 52.9%. Among the most visited websites globally, this rate of growth falls only behind Instagram (#6) at 89.1% and Twitter (#4) at 67.1%.
Wikipedia (#5), a non-profit website that originated in 2001 by Larry Sanger and Jimmy Wales realized over 30% growth. While large tech companies have only accelerated their market share—Google makes up roughly 90% of the search ad market—several regulatory bodies are placing greater scrutiny on them. An October 2020 antitrust report suggested that Big Tech is in fact anti-competitive, drawing comparisons with oil tycoons of the 19th and 20th centuries. With these key forces in mind, it raises a critical question: is there a limit to their growth? on But fast forward to the end of last week, and SVB was shuttered by regulators after a panic-induced bank run. So, how exactly did this happen? We dig in below.
Road to a Bank Run
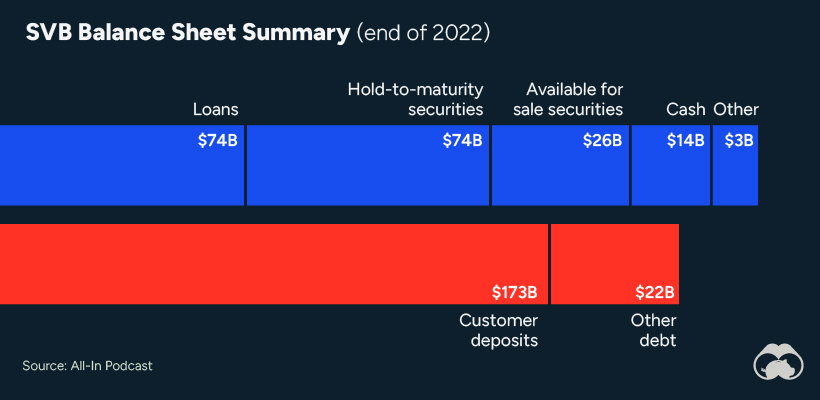
SVB and its customers generally thrived during the low interest rate era, but as rates rose, SVB found itself more exposed to risk than a typical bank. Even so, at the end of 2022, the bank’s balance sheet showed no cause for alarm.
As well, the bank was viewed positively in a number of places. Most Wall Street analyst ratings were overwhelmingly positive on the bank’s stock, and Forbes had just added the bank to its Financial All-Stars list. Outward signs of trouble emerged on Wednesday, March 8th, when SVB surprised investors with news that the bank needed to raise more than $2 billion to shore up its balance sheet. The reaction from prominent venture capitalists was not positive, with Coatue Management, Union Square Ventures, and Peter Thiel’s Founders Fund moving to limit exposure to the 40-year-old bank. The influence of these firms is believed to have added fuel to the fire, and a bank run ensued. Also influencing decision making was the fact that SVB had the highest percentage of uninsured domestic deposits of all big banks. These totaled nearly $152 billion, or about 97% of all deposits. By the end of the day, customers had tried to withdraw $42 billion in deposits.
What Triggered the SVB Collapse?
While the collapse of SVB took place over the course of 44 hours, its roots trace back to the early pandemic years. In 2021, U.S. venture capital-backed companies raised a record $330 billion—double the amount seen in 2020. At the time, interest rates were at rock-bottom levels to help buoy the economy. Matt Levine sums up the situation well: “When interest rates are low everywhere, a dollar in 20 years is about as good as a dollar today, so a startup whose business model is “we will lose money for a decade building artificial intelligence, and then rake in lots of money in the far future” sounds pretty good. When interest rates are higher, a dollar today is better than a dollar tomorrow, so investors want cash flows. When interest rates were low for a long time, and suddenly become high, all the money that was rushing to your customers is suddenly cut off.” Source: Pitchbook Why is this important? During this time, SVB received billions of dollars from these venture-backed clients. In one year alone, their deposits increased 100%. They took these funds and invested them in longer-term bonds. As a result, this created a dangerous trap as the company expected rates would remain low. During this time, SVB invested in bonds at the top of the market. As interest rates rose higher and bond prices declined, SVB started taking major losses on their long-term bond holdings.
Losses Fueling a Liquidity Crunch
When SVB reported its fourth quarter results in early 2023, Moody’s Investor Service, a credit rating agency took notice. In early March, it said that SVB was at high risk for a downgrade due to its significant unrealized losses. In response, SVB looked to sell $2 billion of its investments at a loss to help boost liquidity for its struggling balance sheet. Soon, more hedge funds and venture investors realized SVB could be on thin ice. Depositors withdrew funds in droves, spurring a liquidity squeeze and prompting California regulators and the FDIC to step in and shut down the bank.
What Happens Now?
While much of SVB’s activity was focused on the tech sector, the bank’s shocking collapse has rattled a financial sector that is already on edge.
The four biggest U.S. banks lost a combined $52 billion the day before the SVB collapse. On Friday, other banking stocks saw double-digit drops, including Signature Bank (-23%), First Republic (-15%), and Silvergate Capital (-11%).
Source: Morningstar Direct. *Represents March 9 data, trading halted on March 10.
When the dust settles, it’s hard to predict the ripple effects that will emerge from this dramatic event. For investors, the Secretary of the Treasury Janet Yellen announced confidence in the banking system remaining resilient, noting that regulators have the proper tools in response to the issue.
But others have seen trouble brewing as far back as 2020 (or earlier) when commercial banking assets were skyrocketing and banks were buying bonds when rates were low.