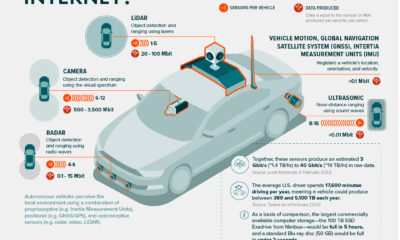
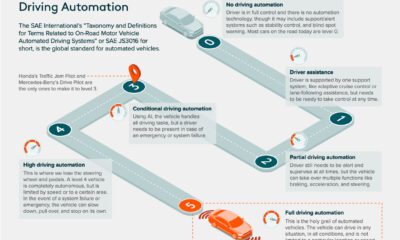
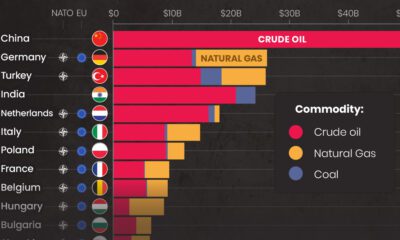
Because of this, automakers are always looking for clever ways to improve gas mileage in their cars. Beating the competition by even the slimmest of margins can give valuable bragging rights within a segment. In this infographic, we’ve used data from the EPA’s 2022 Automotive Trends Report to list off the most fuel efficient cars from 1975 to today. Editor’s note: This is from a U.S. government agency, so the data shown skews towards cars sold in North America.
Data Overview
All of the information in the above infographic is listed in the table below. Data was only available in 5-year increments up until 2005, after which it switches to annual. From this dataset, we can identify three distinct approaches to maximizing fuel efficiency.
Downsizing
Prior to 2000, the best way for automakers to achieve good fuel efficiency was by downsizing. Making cars smaller (lighter) meant they could also be fitted with very small engines. For example, the 1985 Chevrolet Sprint was rated at 49.6 MPG, but had a sluggish 0-60 time of 15 seconds.
Hybrids
The 2000s saw the introduction of mass-market hybrid vehicles like the Honda Insight and Toyota Prius. By including a small battery to support the combustion engine, automakers could achieve good MPGs without sacrificing so heavily on size. While the Insight achieved better fuel economy than the Prius, it was the latter that became synonymous with the term “hybrid”. This was largely due to the Prius’ more practical 4-door design. The following table compares annual U.S. sales figures for both models. Insight sales have fluctuated drastically because Honda has produced the model in several short spans (1999-2006, 2009-2014, 2018-2022). Source: goodcarbadcar.net The Prius may have dominated the hybrid market for a long time, but it too has run into troubles. Sales have been declining since 2014, even setting historic lows in recent years. There are several reasons behind this trend, with one being a wider availability of hybrid models from other brands. We also can’t ignore the release of the Tesla Model 3, which began shipping to customers in 2017.
Electric Vehicles
We’re currently in the middle of a historic transition to electric vehicles. However, because EVs do not use fuel, the EPA had to develop a new system called MPGe (miles per gallon of gasoline-equivalent). This new metric gives us the ability to compare the efficiency of EVs with traditional gas-powered cars. An underlying assumption of MPGe is that 33.7 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity is comparable to the energy content of a gallon of fuel. The most fuel efficient car you can buy today is the 2023 Lucid Air, which achieves 140 MPGe. Close behind it is the 2023 Tesla Model 3 RWD, which is rated at 132 MPGe. Check out this page to see the EPA’s top 10 most efficient vehicles for 2023. on These faulty airbags, installed by 19 different automakers including BMW and Toyota from 2002 to 2015, can explode when deployed and have led to numerous tragic accidents. Their recall affected 67 million airbags (including Honda’s vehicles above) and has been known as the largest safety recall in U.S. history. Over the past four decades, there have been over 22,000 automobile recalls in the United States. In this interactive piece, Chimdi Nwosu uses data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration to visualize the types of automobile recalls over the past 40 years, the companies with the most recalls, the components that were recalled the most, and, most importantly, their impacts on people.
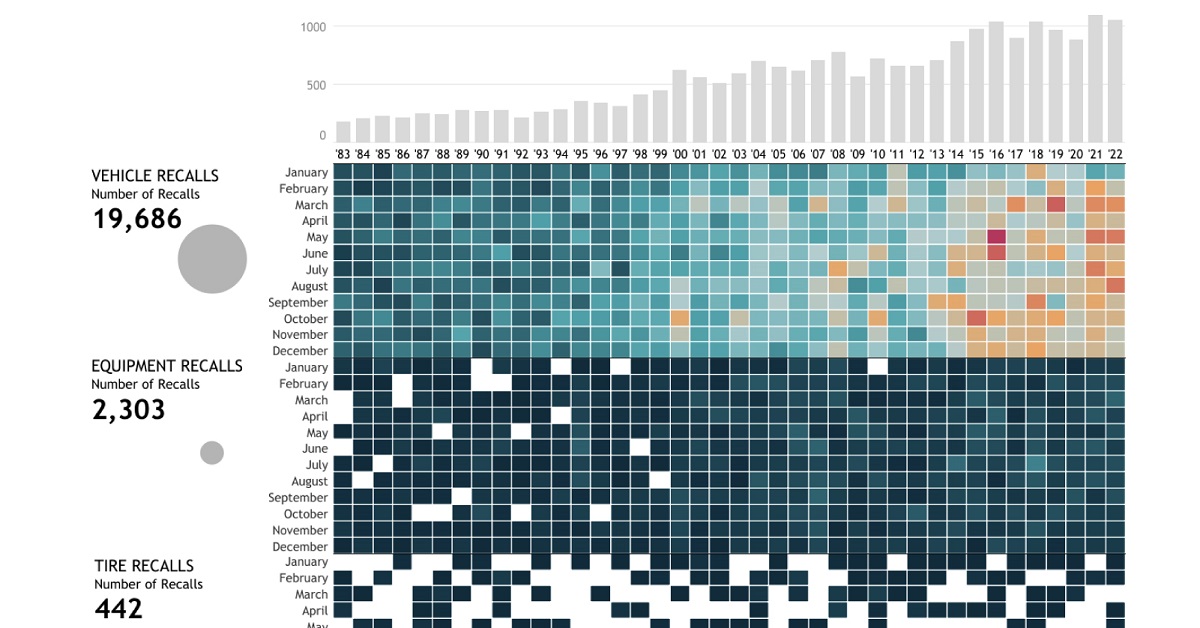
Breaking Down U.S. Automobile Recalls
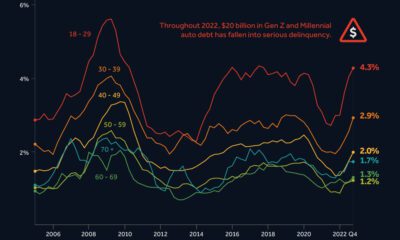
Whether a recall affects specific vehicle components, equipment, or vehicles as a whole, it affects the lives of millions of automobile users. When combined, these numbers ramp up exponentially. The U.S. alone has seen a total of 22,651 recalls over the past 40 years, impacting more than one billion people. Almost 72% of these people were affected by nearly 20,000 vehicle recalls, while around 19% were impacted by over 2,000 equipment recalls during this period. Comparatively, the 442 tire recalls and 220 child seat recalls affected significantly less, but still a total of 96.9 million people. While an inconvenience to many, the recall of these faulty vehicle parts saves many more from unfortunate incidents that may have occurred if left unchecked.
Minor and Major Recalls
One of the largest recalls in history took place in 2014 when General Motors—the manufacturer with the highest total of recalls in four decades—recalled millions of vehicles including the 2005-2007 Chevrolet Cobalt, 2007 Pontiac G5, and 2006-2007 Chevrolet HHR, amongst others. The reason for this recall was a faulty ignition switch that caused the vehicle’s engine to shut down while driving, disabling safety systems including airbags. This fault led to the death of hundreds of people. However, not all recalls are this severe. BMW, for example, recalled just four vehicles in December last year because one of the four bolts in the driver’s backrest was not attached properly. Similarly in 2020, Ford recalled some of its vehicles due to a faulty door latch. While this recall inconvenienced over two million users, it was less likely to lead to severe consequences if left unchecked.
A Safer Future?
The number of automobile recalls over the past four decades has seen a steep rise. As have car safety standards. While recalls could hint at the risks involved in taking your car out for a drive, they also indicate manufacturers taking responsibility for their faulty commodities, and affect a very small percentage of vehicles on the road. To improve automobile safety, the NHTSA proposed a New Car Assessment Program in 2022, which provides vehicle users with safety ratings for every new vehicle. This five-star safety rating program rates the vehicles’ safety features, crashworthiness, and resistance to rollover. With self-driving cars now also entering the mix, we need to stay informed about vehicle safety to keep our vehicles, our streets, and ourselves safe in the future.