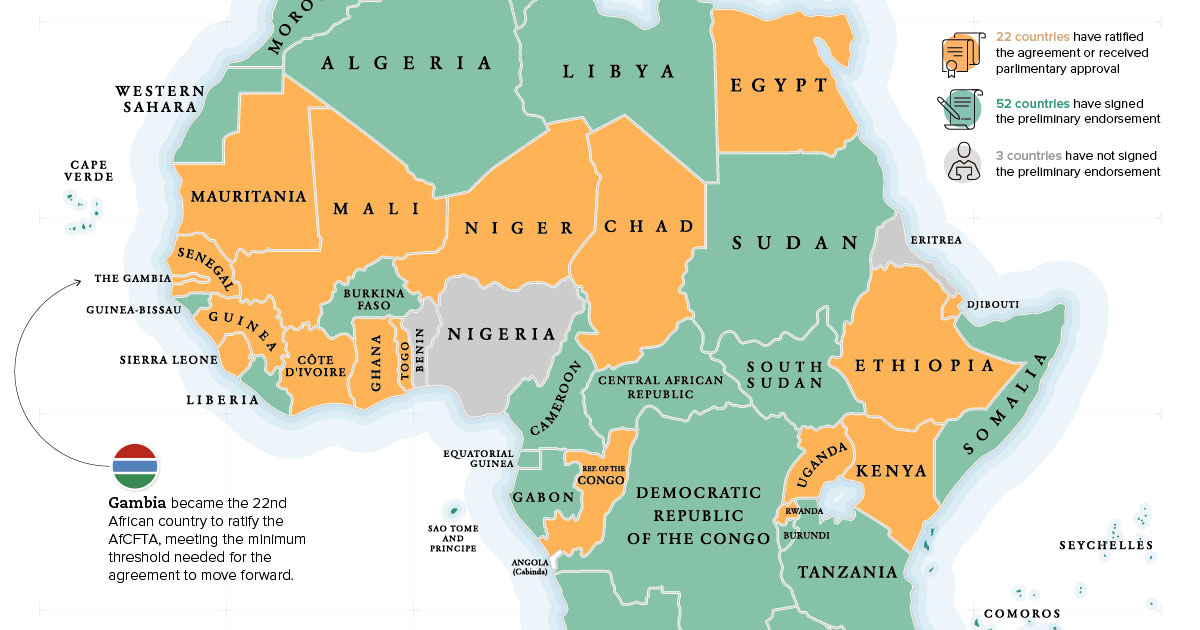
To this end, nations in the region have been working towards an ambitious plan to create the world’s largest trade area. The Gambia recently became the latest country to ratify the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), helping the agreement reach critical mass to move forward. Today’s graphic helps put the region – and the status of AfCFTA – into perspective.
The Patchwork Problem
One key to unlocking the region’s economic potential is making it easier for Africa’s 55 countries to trade with one another. Currently, Africa is a patchwork of regulations and tariffs, and trade between countries has suffered as a result. For example, only 10% of Nigeria’s annual trade activity is with other African countries. This is a surprising given the country’s dominant economic standing and location firmly in the center of the continent. As a whole, Africa’s intra-continental trade level hovers at just around 20%, while nations in Europe and Asia are at 69% and 59%, respectively. Clearly, there is a lot of room for growth.
What is AfCFTA?
AfCFTA is the biggest free trade agreement since the establishment of the World Trade Organization. The objective of the agreement is to create a single continental market for goods and services, with free movement of business people and investments. Last year, 44 African leaders signed an agreement to ratify AfCFTA, with half that number needed to move the agreement forward. Earlier this week, The Gambia was the 22nd country to announce that its government has ratified the agreement, meeting the threshold to officially put the wheels in motion. – Mark-Anthony Johnson, CEO, JIC Holdings The good news for the agreement is that many of Africa’s largest economies – including Egypt and South Africa – are already on board. There is, however, one significant holdout.
The Elephant in the Room
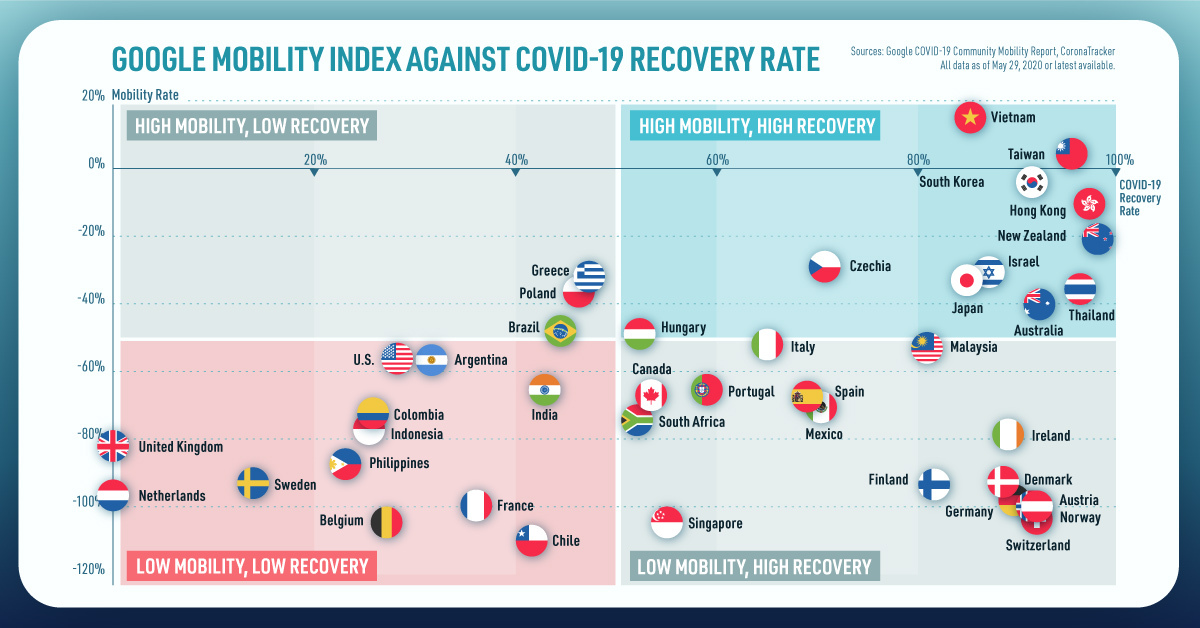
Even though the threshold for pushing AfCFTA forward has been reached, Nigeria’s lack of commitment is still a major blow to the strength and credibility of the agreement. Nigeria’s situation is complicated. The country’s economic prospects are bright, and Lagos is on a trajectory to become the world’s largest city over the next few decades. On the other hand, there is fierce opposition from labor unions, and the country is home to largest concentration of people living in extreme poverty in the world. – Ayuba Wabba, President of NLC, Nigeria’s largest labor union While the majority of African nations appear to be on board with the plan to enact AfCFTA, it remains to be seen whether Nigeria comes along for the ride or decides to go it alone. on Today’s chart measures the extent to which 41 major economies are reopening, by plotting two metrics for each country: the mobility rate and the COVID-19 recovery rate: Data for the first measure comes from Google’s COVID-19 Community Mobility Reports, which relies on aggregated, anonymous location history data from individuals. Note that China does not show up in the graphic as the government bans Google services. COVID-19 recovery rates rely on values from CoronaTracker, using aggregated information from multiple global and governmental databases such as WHO and CDC.
Reopening Economies, One Step at a Time
In general, the higher the mobility rate, the more economic activity this signifies. In most cases, mobility rate also correlates with a higher rate of recovered people in the population. Here’s how these countries fare based on the above metrics. Mobility data as of May 21, 2020 (Latest available). COVID-19 case data as of May 29, 2020. In the main scatterplot visualization, we’ve taken things a step further, assigning these countries into four distinct quadrants:
1. High Mobility, High Recovery
High recovery rates are resulting in lifted restrictions for countries in this quadrant, and people are steadily returning to work. New Zealand has earned praise for its early and effective pandemic response, allowing it to curtail the total number of cases. This has resulted in a 98% recovery rate, the highest of all countries. After almost 50 days of lockdown, the government is recommending a flexible four-day work week to boost the economy back up.
2. High Mobility, Low Recovery
Despite low COVID-19 related recoveries, mobility rates of countries in this quadrant remain higher than average. Some countries have loosened lockdown measures, while others did not have strict measures in place to begin with. Brazil is an interesting case study to consider here. After deferring lockdown decisions to state and local levels, the country is now averaging the highest number of daily cases out of any country. On May 28th, for example, the country had 24,151 new cases and 1,067 new deaths.
3. Low Mobility, High Recovery
Countries in this quadrant are playing it safe, and holding off on reopening their economies until the population has fully recovered. Italy, the once-epicenter for the crisis in Europe is understandably wary of cases rising back up to critical levels. As a result, it has opted to keep its activity to a minimum to try and boost the 65% recovery rate, even as it slowly emerges from over 10 weeks of lockdown.
4. Low Mobility, Low Recovery
Last but not least, people in these countries are cautiously remaining indoors as their governments continue to work on crisis response. With a low 0.05% recovery rate, the United Kingdom has no immediate plans to reopen. A two-week lag time in reporting discharged patients from NHS services may also be contributing to this low number. Although new cases are leveling off, the country has the highest coronavirus-caused death toll across Europe. The U.S. also sits in this quadrant with over 1.7 million cases and counting. Recently, some states have opted to ease restrictions on social and business activity, which could potentially result in case numbers climbing back up. Over in Sweden, a controversial herd immunity strategy meant that the country continued business as usual amid the rest of Europe’s heightened regulations. Sweden’s COVID-19 recovery rate sits at only 13.9%, and the country’s -93% mobility rate implies that people have been taking their own precautions.
COVID-19’s Impact on the Future
It’s important to note that a “second wave” of new cases could upend plans to reopen economies. As countries reckon with these competing risks of health and economic activity, there is no clear answer around the right path to take. COVID-19 is a catalyst for an entirely different future, but interestingly, it’s one that has been in the works for a while. —Carmen Reinhart, incoming Chief Economist for the World Bank Will there be any chance of returning to “normal” as we know it?